Request A Quote
Our business is most valuable when it helps our customers. Please fill out the form with as much detail as possible so we can respond with the most helpful solution.

Yuji supplies eco-friendly insulating gases for medium voltage (MV) to high voltage (HV) electric power systems in gas insulated equipment (GIE), such as switchgear (GIS), circuit breakers, transmission lines (GIL), substations, and more! Our team of experts have developed SF6 gas and sustainable alternatives with zero ODP and very low GWP, such as C4F7N (C4 gas) and C5F10O (C5 gas) with great dielectric strength and excellent arc-quenching properties. Partner with Yuji to support a greener power industry future based on advanced fluorine chemistry.
The power grid delivers electricity from power plants to homes and businesses across the nation. Its vast network of power generation, transmission, and delivery enables all of our devices, electronics, and electric automobiles to function. In the 1800s, Thomas Edison revealed the country’s first power plant at the Pearl Street Station in Manhattan, New York City. Since then, electric power grids have reached every nook and cranny of the United States to power our day to day life.
Through the interconnectivity of the power industry, American society has evolved immensely- however, powering all of America is no easy job.
Grids are designed to supply electricity to industries and communities in large quantities and often times at very high voltages. In order to manage this, electrical transmission equipment use insulating material to convert the electricity’s voltage and protect the equipment that enables this function. Since the 1960’s, dielectric gases such as SF6 have been the preferred insulating material that is used due to its high electrical insulating properties, non-flammability, and non-toxicity.
Dielectric gas is a type of gas used as an electrical insulator in industrial applications. The most often used gases are air, nitrogen, and sulfur hexafluoride. The existence of a dielectric gas is necessary for a number of electrical components, including transformers and circuit breakers, to avoid damage to a circuit in the event of an electrical discharge. Its major objective is to stop or quickly stop electric discharges. In high voltage applications such as transformers, circuit breakers (specifically sulfur hexafluoride circuit breakers), switchgear (specifically high voltage switchgear), radar waveguides, etc., dielectric gases are employed as electrical insulators, i.e insulating gases.
High dielectric strength, high thermal stability, chemical inertness towards the building materials being used, non-flammability and low toxicity, low boiling point, good heat transmission capabilities, and low cost are all desirable qualities in an insulating gas.
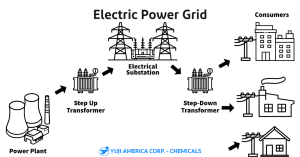
The network of electrical grid components are:
Power Stations: also known as power plant or generating station; many power stations function by burning fossil fuels, like coal, oil, and natural gas to generate electricity. Other plants function on nuclear power or renewable energy sources like solar, wind, hydroelectric, or geothermal.
Electrical Substation: this part of the network serves to transform voltage from high to low or vice versa; A substation may also include transformers to adjust voltage levels between high transmission voltages and lower distribution voltages, or at the interconnection of two different transmission voltages.
Electrical Power Transmission: a set of interconnected lines that often span very long distances, to carry high voltage electrical power from a power plant to a substation.
Electric Power Distribution: the final stage in the network that delivers electric power to the consumer. This is done with the help of transformers, in substations and primary distribution lines, which lower transmission voltage to the required level to power your space.
SF6, Sulfur Hexafluoride, is commonly used as an electrical insulator in high voltage equipment that transmits and distributes electricity. The U.S electric power industry has used SF6 in circuit breakers, gas-insulated substations, and other switchgear used in the transmission system to manage the high voltages carried between generating stations and customer load centers.
The choice of insulating gas is mostly determined by the voltage level of the circuit and device, as well as the gas’s fundamental chemical and thermal characteristics, such as its boiling point and heat-transfer capabilities. It is also necessary to take into account the dielectric gas’s level of toxicity and flammability under specific circumstances. A high-voltage transformer, for example, may experience physical deterioration as a result of an electrical short circuit, resulting in the release of gas into the environment. Because they are mostly inert and nonreactive, air and nitrogen gasses are frequently employed for this reason.
Industrial circuit breakers that connect generators to step-up voltage transformers employ sulfur hexafluoride as a dielectric gas in high-voltage switchgear. Additionally, it is employed in high voltage electric power system components including transmission lines, transformers, and substations that call for gas insulators. Due to its outstanding insulating properties and capacity to reduce radio wave and sound wave transmission from electrical equipment, around 80% of all sulfur hexafluoride produced is typically utilized in electrical power plants and substations around the world.
Electrical arcs can develop in electrical power systems, such as switchgear, and because to SF6’s high electronegativity and heat-transferring capabilities, the arc temperature can be reduced. Electron avalanches and flashovers can be efficiently avoided by using SF6 gas and free electrons. Additionally, it has the highest breakdown voltage of any insulating gas, which is the voltage at which a dielectric gas starts to conduct current instead of functioning as an insulator.
Electrical discharges cause SF6 to partially break down, and as a result, oxygen, moisture, and breakdown products such sulphur dioxide may be produced. SF6 gas has the unusual capacity to “self-heal” following the discharge, unlike other insulating materials. Its broad use in the electrical industry is due in part to this.
It’s crucial to analyze SF6 gas on a regular basis. Throughout the equipment’s lifespan, routine periodic maintenance must be performed. This guarantees the safety of both people and equipment.
|
Gas |
Formula |
Properties |
|
Sulfur Hexafluoride |
SF6 |
Excellent insulating properties but high global warming potential. |
|
Nitrogen |
N2 |
Often mixed with other insulators, however effective in slowing electrons making it ideal for electrical insulation. |
|
Air |
Mixture |
Utilized due to low cost and availability, with effective insulating properties. |
|
Oxygen |
O2 |
Poor conductor of heat, which helps facilitate combustion. Poor conductor of electricity which results in effective insulating properties. |
|
Nitrous Oxide |
N2O |
Weak electron-attaching and slows down electrons, making it ideal for electrical insulating. |
Electrical arcs can develop in electrical power systems, such as switchgear, and because to SF6’s high electronegativity and heat-transferring capabilities, the arc temperature can be reduced. Electron avalanches and flashovers can be efficiently avoided by using SF6 gas and free electrons. Additionally, it has the highest breakdown voltage of any insulating gas, which is the voltage at which a dielectric gas starts to conduct current instead of functioning as an insulator.
Electrical discharges cause SF6 to partially break down, and as a result, oxygen, moisture, and breakdown products such sulphur dioxide may be produced. SF6 gas has the unusual capacity to “self-heal” following the discharge, unlike other insulating materials. Its broad use in the electrical industry is due in part to this.
It’s crucial to analyze SF6 gas on a regular basis. Throughout the equipment’s lifespan, routine periodic maintenance must be performed. This guarantees the safety of both people and equipment.
Sulfur hexafluoride has some drawbacks as a dielectric gas, though, and efforts are being undertaken to mix it with safer gases like nitrogen, carbon dioxide, or perfluorocarbon compounds. When released into the atmosphere, sulfur hexafluoride is thought to contribute to global warming 22,800 to 23,900 times more than an equivalent amount of carbon dioxide. The substance also has significant health hazards when inhaled by people, including the possibility of respiratory issues. When discharged into the air, the substance frequently mixes with other substances, which can result in fluoride contamination of the body and a number of illnesses. As mentioned in our article, “What Are Ozone-Depleting Substances,” gases with a high greenhouse effect index are identified by government agencies and then regulated across the nation.
The Kyoto Protocol, an international pact between states, went into effect in 2005 requiring reductions in greenhouse gas emissions on a country-by-country basis. SF6 gas has the potential to linger in the atmosphere for thousands of years due to its chemical stability. As a result, the accord and other regulations have designated it as a greenhouse gas and sets a cap on how much can be released into the environment.
Yuji has developed sustainable insulating gases for electric power systems to help support the industry’s transition to eco-friendly chemical alternatives.
Sulfur Hexafluoride |
Perfluoroisobutyronitrile |
Perfluoro(3-methyl-2-butanone) |
|
SF6 |
C4F7N |
C5F10O |
|
Insulating and arc-extinguishing gas for high voltage electric power equipment. |
Insulating and arc-extinguishing gas with 0 ODP and low GWP. |
Insulating and arc-extinguishing gas with 0 ODP and low GWP. |
LEARN MORE |
LEARN MORE |
LEARN MORE |
Previous Precision Cleaning
Our business is most valuable when it helps our customers. Please fill out the form with as much detail as possible so we can respond with the most helpful solution.